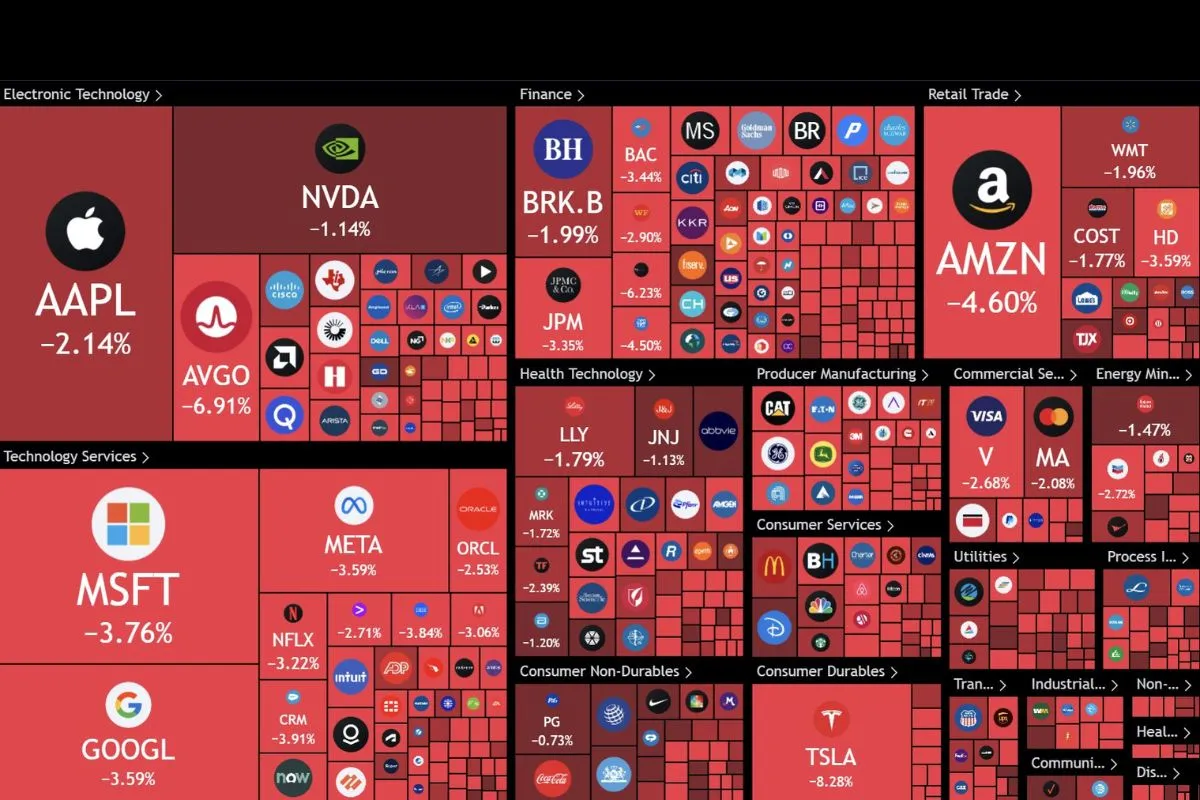
Over $1.50 trillion was wiped out from the US stock market following Fed’s cautious rate cut projections. Explore causes and implications for investors!
In a shocking turn of events, the US stock market experienced a catastrophic decline on December 18, 2024, resulting in over $1.50 trillion being wiped out from the market capitalization of publicly traded companies. This significant drop has raised concerns among investors and market analysts alike, prompting discussions about the underlying factors contributing to this downturn and its potential implications for the economy.
The Market Collapse: Key Figures
The decline marked one of the steepest losses in recent history, with major indices suffering substantial blows:
- The Dow Jones Industrial Average plummeted by 1,103 points, or 2.54%, closing at 42,326.87.
- The S&P 500 fell by 3.03%, settling at 5,872.16.
- The Nasdaq Composite dropped by 3.74%, finishing at 19,392.69.
These figures illustrate a broad-based sell-off that affected nearly every sector of the market, with particularly severe impacts on technology and consumer discretionary stocks.
Causes Behind the Decline
The primary catalyst for this dramatic decline was the Federal Reserve’s recent announcement regarding its monetary policy outlook. During a press conference, Fed Chair Jerome Powell indicated that the central bank would likely implement only two interest rate cuts in 2025, a significant reduction from earlier expectations of four cuts. This news came as a shock to investors who had anticipated a more aggressive easing of monetary policy.
Key Factors Contributing to Market Sentiment:
- Revised Rate Cut Projections: The Fed’s decision to scale back its forecast for interest rate cuts has led to increased uncertainty in the markets. Investors had been betting on a more favorable monetary environment that would support economic growth and boost stock prices.
- Rising Inflation Concerns: Alongside the announcement of fewer rate cuts, the Fed projected that inflation would remain higher than previously expected. This news has heightened fears of persistent inflationary pressures, which could erode consumer purchasing power and corporate profitability.
- Surge in Treasury Yields: Following the Fed’s announcement, Treasury yields surged, with the yield on 10-year notes touching a seven-month high of over 4.50%. Higher yields typically make bonds more attractive compared to stocks, leading to capital outflows from equity markets.
- Sector-Specific Weakness: Sectors particularly sensitive to interest rates, such as real estate and consumer discretionary, experienced sharp declines. Major companies like Amazon and Tesla saw their stock prices drop significantly as investors reassessed their valuations in light of changing economic conditions.
Market Reactions and Investor Sentiment
The immediate aftermath of the Fed’s announcement saw a spike in volatility across financial markets. The Cboe Volatility Index (VIX), often referred to as Wall Street’s “fear gauge,” surged as investors grappled with uncertainty about future economic conditions and interest rate policies.
Market analysts have noted that this sell-off reflects a broader shift in investor sentiment from optimism to caution. Many are now reassessing their portfolios and strategies in light of the new economic landscape shaped by tighter monetary policy.
Implications for the Economy
The significant decline in stock market value raises important questions about its potential impact on the broader economy:
- Consumer Confidence: A declining stock market can negatively affect consumer confidence, leading to reduced spending and investment. As household wealth diminishes due to falling stock prices, consumers may become more cautious with their expenditures.
- Corporate Financing: Companies that rely on equity markets for financing may face challenges as investor sentiment shifts. A volatile stock market can complicate capital-raising efforts through public offerings or secondary equity sales.
- Economic Growth Projections: Analysts are now revising their growth projections for 2025 based on the Fed’s updated outlook and market conditions. Slower growth could translate into lower corporate earnings and further declines in stock valuations.
Looking Ahead: What’s Next for Investors?
As investors navigate this turbulent period, several key considerations will shape their strategies:
- Monitoring Economic Indicators: Keeping an eye on inflation rates, employment data, and consumer spending will be crucial in assessing future market movements.
- Diversification Strategies: Investors may seek to diversify their portfolios by including assets that typically perform well during periods of economic uncertainty, such as commodities or defensive stocks.
- Long-Term Perspective: While short-term volatility can be unsettling, maintaining a long-term investment perspective may help investors weather market fluctuations without making impulsive decisions.
The recent wipeout of over $1.50 trillion from the US stock market underscores the fragility of investor sentiment amid changing economic conditions and monetary policy expectations. As analysts continue to dissect the implications of these developments, it is clear that both individual investors and institutional players will need to adapt their strategies in response to this evolving landscape.
While uncertainty looms large over financial markets, history shows that periods of volatility can also present opportunities for astute investors willing to navigate challenges with a long-term view.