As Tesla leads the charge in the electric vehicle (EV) market with significant strides in autonomy and sales, many legacy automakers face mounting challenges. An analysis by Auto Blog has sounded alarms for traditional automakers, warning that up to 20 major brands may struggle to survive the shift to electric vehicles. With factors like declining EV demand, economic pressures, and growing competition from Chinese manufacturers, these automakers could be at risk.
Key Challenges Facing Legacy Automakers
The transition to electric vehicles presents specific challenges for legacy car manufacturers, who are entrenched in traditional processes and have invested heavily in producing internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles.
Although these ICE models generate profits, allowing some funds for EV innovation, these brands also struggle to fully commit to new EV manufacturing processes. This divide between past and future technologies may hamper their ability to produce EVs at a scale and price competitive with dedicated EV manufacturers like Tesla and BYD.
The Hybrid Conundrum
Many legacy automakers have chosen hybrids as an “interim” solution, leveraging this technology to transition away from ICE without going all-in on EVs. However, critics argue that focusing on hybrids delays the inevitable need to transition to full electric, losing valuable time that could have been dedicated to developing competitive EV technology and infrastructure.
At-Risk Legacy Brands in the EV Market
Auto Blog’s report listed several brands that may struggle to survive the EV transformation. Here’s a look at some prominent names and their current positions:
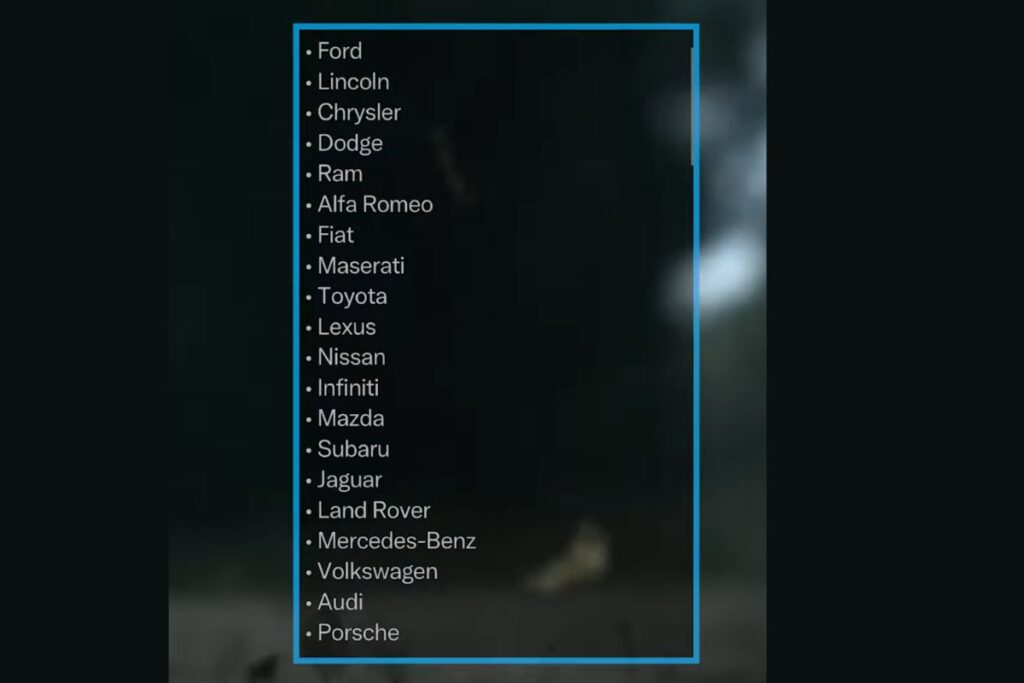
- Ford: Despite the popularity of its Mustang Mach-E, Ford has struggled with production issues, notably delaying production of its F-150 Lightning and postponing its three-row EV SUV. While Ford has made strides, it remains uncertain if they can fully commit to the changes necessary to remain competitive.
- Lincoln: Ford’s luxury division, Lincoln, currently has no fully electric vehicles, placing it well behind competitors in a market increasingly dominated by luxury EVs.
- Chrysler: With only a single hybrid minivan on the market, Chrysler’s EV offerings are limited, and it has yet to demonstrate a comprehensive EV strategy, making its future in the EV era uncertain.
- Dodge: Known for its powerful ICE models, Dodge has yet to release a notable EV. Whether its fans will embrace an electric version remains to be seen.
- Toyota: While Toyota has been a leader in hybrid technology, the company has yet to release a fully competitive EV, despite the growing demand. The brand’s commitment to alternative technologies, like hydrogen, further divides its focus, potentially stalling its electric future.
- Nissan: Recently cutting both production forecasts and jobs, Nissan is struggling. Despite some early success with the Nissan Leaf, it now trails other EV leaders, both in innovation and sales.
EV Startups: Benefits and Risks
EV startups have their own challenges, primarily with scaling production and making vehicles affordable for mainstream consumers. Some early EV startups, such as Fisker, have struggled financially and faced setbacks. By contrast, Tesla’s success is attributed to its decade-long head start and innovative business model, including direct-to-consumer sales and advanced software integration.
Pressure from Chinese Automakers
Chinese automakers, led by BYD, are proving fierce competition with affordable EVs. However, while Chinese brands dominate their home market, they face challenges entering Western markets due to tariffs and protectionist policies.
For example, Canada recently imposed a 100% tariff on Chinese EVs, leading BYD to reconsider its planned expansion into the Canadian market. Nonetheless, Chinese brands are making strides in Europe and could see greater success there.
Tesla’s Unique Position in the EV Market
Tesla has emerged as a leader in the EV market, expanding rapidly both in production and market share. Unlike legacy brands, Tesla’s business model, international production capacity, and focus on autonomy and software integration give it a distinct advantage. Tesla’s ability to streamline production and consistently innovate further highlights the challenges faced by traditional manufacturers attempting to catch up.
The European Dilemma and Tariffs Impact
The EV market in Europe presents additional challenges for legacy automakers. Many European automakers have closed plants and reduced workforce due to lost market share in China. Furthermore, Chinese EVs are moving into European markets, thanks to fewer trade barriers.
In contrast, U.S. policies under leaders like former President Donald Trump have implemented tariffs and other measures, effectively blocking Chinese brands from entering.
The transition to EVs is not just a technological shift but a complete overhaul of the auto industry. Legacy brands that can’t adapt to the new business models and production strategies required for electric vehicles may not survive.
While Tesla and a few other EV-focused brands continue to lead, many traditional automakers find themselves at a crossroads, struggling to balance current ICE profits with the demands of an electric future. The next decade will reveal which brands can pivot and innovate—and which will become casualties of the “EV Apocalypse.”